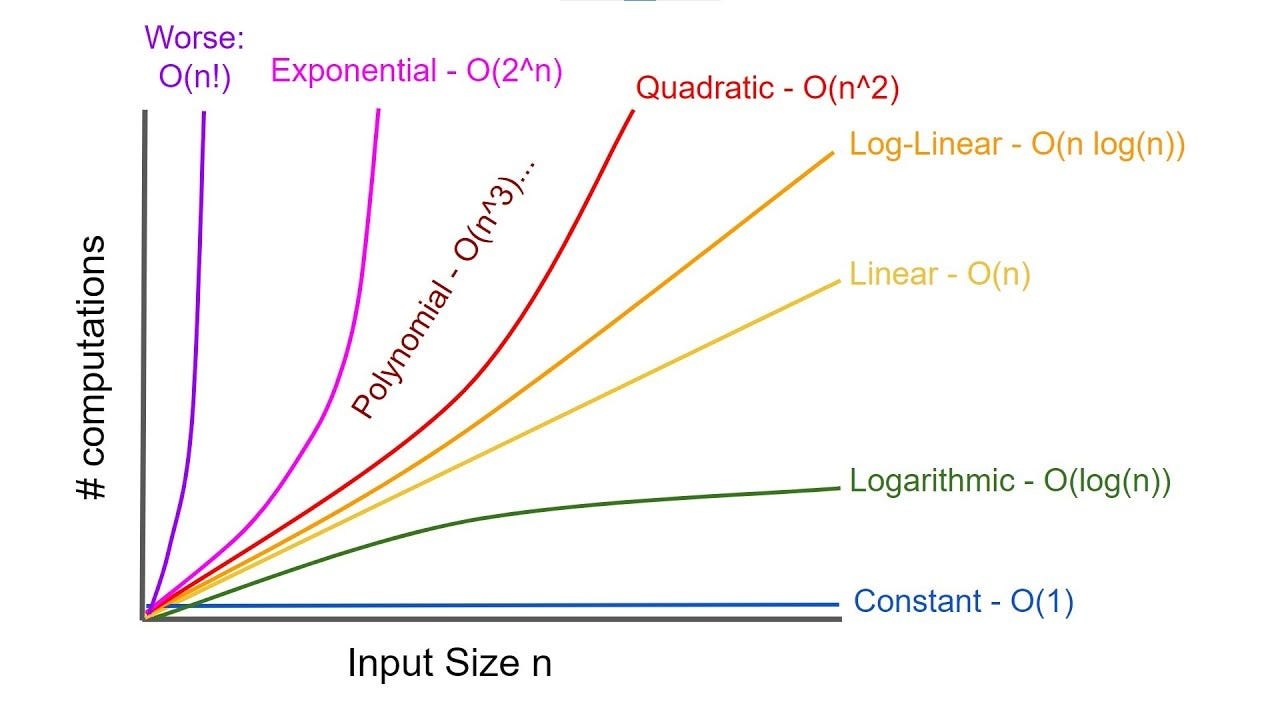
🔍 What Is Big O Notation?
Big O notation describes how an algorithm’s performance scales as the size of the input increases.
It focuses on the worst-case scenario and ignores constants or low-order terms.
📚 Big O Cheatsheet (with Examples)
| Notation | Name | Example | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
O(1) | Constant Time | access array[i] | Doesn’t grow with input size |
O(log n) | Logarithmic Time | binary search | Cuts the input in half each time |
O(n) | Linear Time | loop through array | Grows directly with input size |
O(n log n) | Linearithmic Time | merge sort, quick sort | Logarithmic + linear |
O(n²) | Quadratic Time | nested loops | Grows with square of input size |
O(2ⁿ) | Exponential Time | recursive Fibonacci | Doubles with each addition to input |
O(n!) | Factorial Time | brute-force permutations | Extremely inefficient for large input |
🧠 Why It Matters
-
Helps you compare algorithms.
-
Crucial for optimization and scaling.
-
Often tested in coding interviews.
🧾 Big O Examples in Python
# O(1) – Constant Time
def get_first_element(arr):
return arr[0]
# O(n) – Linear Time
def print_all(arr):
for item in arr:
print(item)
# O(n²) – Quadratic Time
def print_pairs(arr):
for i in arr:
for j in arr:
print(i, j)
# O(log n) – Logarithmic Time
def binary_search(arr, target):
low = 0
high = len(arr) - 1
while low <= high:
mid = (low + high) // 2
if arr[mid] == target:
return mid
elif arr[mid] < target:
low = mid + 1
else:
high = mid - 1
return -1